Blocked Retinal Artery
Retinal Artery Occlusion
01
What Is Retinal Artery Occlusion?
A retinal artery occlusion occurs when the central retinal artery or one of the arteries that branch off of it becomes blocked. This blockage is typically caused by a tiny embolus (clot) in the blood stream. The occlusion decreases the oxygen supply to the area of the retina nourished by the affected artery, causing permanent vision loss.
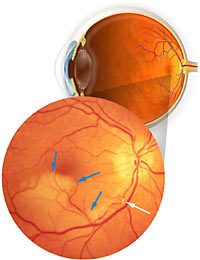
In this photograph, the affected area of the retina is the pale, whitish-yellow region (blue arrows) that is normally supplied by the blocked artery (white arrow). The surrounding reddish-orange area is healthy retina tissue.
02
Signs And Symptoms Of Artery Occlusion
- Transient loss of vision prior to the artery occlusion (in some cases)
- Sudden, painless and complete loss of vision in one eye (Central artery occlusion)
- Sudden, painless, partial loss of vision in one eye (Branch artery occlusion)
Artery occlusion is diagnosed by examining the retina with an ophthalmoscope.
03
Treatment Of Artery Occlusion
Unfortunately, there is no treatment that can consistently restore vision lost from an artery occlusion. However, if it is caught within the first hour and treatment is initiated immediately, recovery is possible in rare cases.
The following conditions increase the risk of problems that may affect the vessels of the eye:
- High cholesterol
- Heart Disease
- Arteriosclerosis
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Glaucoma
ADDRESSES:
PHONE NUMBERS:
Fax: (877) 717-0096 (toll free)
